Featured Member Video
How to make fire using HanddrillMore Videos by MountanWolf
View larger or ask the author a question.
View all wilderness survival videos
Recent Forum Posts 
Come Join the Discussion Today!
Our site has been mentioned in:
U.S. News and World Report
Best of the Web - Site of the Week 8/6/01
Discovery Channel Canada
One Week in the Wilderness
USA Today
Hot Sites 08/08/2005
How to Build a Susitna Log Cabin
Standing on a hill overlooking the salt meadows at Hunter's Point, L. I., there was an old farmhouse the roof of which projected over both sides of the house four or five feet. The hill on which it stood has been cut away, the meadows which it overlooked have been filled up with the dirt from the hill, and only a surveyor with his transit and the old property-lines map before him could ever find the former location of this house, but it is somewhere among the tracks of the Long Island Railroad.
Opposite the house, on the other side of the railroad track, in the section known as Dutch Kills of Long Island City, two other houses of the same style of architecture stood; they had double doors—that is, doors which were cut in two half-way up so that you might open the top or bottom half or both halves to suit your fancy. The upper panels of these doors had two drop-lights of glass set in on the bias, and between them, half-way down the upper half, was a great brass knocker with a grip big enough to accommodate both hands in case you really wanted to make a noise.
There was another house of this same description in the outskirts of Hoboken, and I often wondered what the origin of that peculiar roof might be. I found this type of house as far north toward the Hudson Bay as the settlements go, and still farther north the Susitna house explains the origin of the overhanging eaves (Fig. 268). Of course the Susitna, as here drawn, is not exactly the same as that built by the natives on the Susitna River, but the end plates (Fig. 263) are the same as those used in the primitive houses of the Northwest.
How to Cut the Tree
Fig. 264 shows a standing fir-tree and also shows what cuts to make in order to get the right-shaped log for an end plate. Fig. 265 shows the method of scoring and hewing necessary in order to flatten the end of the log as it is in Fig. 266. Fig. 267 shows the style in which the natives roof their Susitnas with logs. The elbows at the end of the plates (Fig. 266) serve to keep the logs of the roof (Fig. 267) from rolling off, but the Susitna log cabin which we are building is expected to have a roof (Fig. 268) of thatch or a roof of shingles, because we have passed the rude shacks, sheds, and shelters used for camps and are now building real houses in which we may live. The Susitna may be built of round logs or of flattened logs (le carréage), in which case we can use the General Putnam square notch (Fig. 263) for joining the ends of our logs. In raising the roof, erect the ridge-pole first. The ridge-pole may be set up on two uprights to which it is temporarily nailed, and the upright props may be held in place by the two diagonal props or braces, as shown in Fig. 263. If the logs are squared, cut a small bird's-mouth notch in the rafter where it extends over the side-plate logs of the pen and bevel the top end of your gable rafters to fit against the ridge-pole as in the diagrams. The other rafters are now easily put in place, but if the logs are round you must notch the rafters and side-plates as shown by the diagram between Figs. 263 and 267; the dotted lines show where the rafter and the logs come together. Nail your rafters to your ridge-pole and fasten them to the side-plate with wooden pegs or spikes. The ridge-pole may be allowed to extend, as in Fig. 268, on each side of the cabin or the elbows (Fig. 266) may be attached to each end of the ridge-pole with noses turned up and painted or carved into a fanciful head as in Fig. 268. If the roof is to be shingled, collect a lot of poles about four inches in diameter, flatten them on both sides, and nail them to the rafters not more than two inches apart, allowing the ends of the sticks to extend beyond the walls of the house at least six inches.
Fig. 263. Fig. 264. Fig. 265. Fig. 266. Fig. 267. Fig. 268.
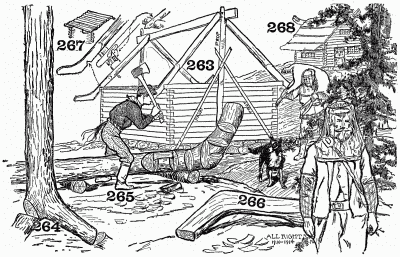 The Susitna log house.
The Susitna log house.
If you desire to make your own shingles, saw up a hemlock, pine, or spruce log into billets of one foot four inches long, then with a froe and a mall (Fig. 179) split the shingles from the billets of wood, or use a broadaxe for the same purpose. Broadaxes are dangerous weapons in the hands of an amateur, but the writer split shingles with a broadaxe upon the shores of Lake Erie when he was but seven years old and, as near as he can count, he still has ten toes and ten fingers. If you intend to thatch the roof you need not flatten the poles which you fasten across the rafters, because the thatch will hide all unevenness of the underpinning. The poles may be laid at right angles to the rafters between six and eight inches apart and the roof thatched as described and illustrated by Fig. 66. The Susitna form of house is the one from which the old Long Island farmhouses were evolved, although the old Long Islanders copied theirs from the homes they left in Holland, but we must remember that even the effete civilization of Europe once had a backwoods country a long, long time ago, and then they built their houses from the timbers hewn in the forests as our own ancestors did in this country; consequently, many of the characteristics of present-day houses which seem to us useless and unnecessary are survivals of the necessary characteristics of houses made of crude material.
Back to Shelters, Shacks, and ShantiesUltimate Survival Knife & Kit |
List Price: 61.99 Our Price: 39.95 |
This 15 inch survival knife with drop point blade features a thick quality stainless steel blade with serrated top edge. Textured and ribbed solid metal handle and guard. Nylon sheath. Survival kit includes a hollow grip with a compass top to store items within the knife itself, as well as additional pouches on the sheath to hold the rest. Complete survival kit. Click Here to Buy the Survival Knife Now. |
|

